Tables
A table presents bound data in a tabular format, where columns represent data fields and rows represent objects. Numerous data management and layout customization features are supported.
All of the data that appears in a table are stored in the table's data sources. Each row template in the table are bound to a data source, and cell templates are bound to fields within a data source. You can present data from multiple data sources within the same table. That is, when you add a new column to a table, simply bind a field to the cell template for the column for each row template. You can also add data sources which not are bound to any row- or cell templates. For example, you can add a data source containing currency exchange rates, and then use these rates for calculating an amount in different currencies.
When you design a table you must consider how to lay out and configure the elements in the table. Generally, you should organize the elements so that users who fill it out can enter data in a logical manner. The table layout designer helps you achieve this goal. In the table layout designer you can add and group columns, add row templates, and bind row- and cell templates to your data sources. Numerous data management and presentation features can be customized for each of the elements in the table.
By designing different views of your table, you can offer users different ways to look at data. For example, you might create a special view that is optimized for printing, or you might create a high-level summary view to eliminate some of the details in a complex table template.
Enabling of built-in commands such as New and Open, and actions and reports available to users in the Task Pane, can be customized for each table.
You can choose between two different layouts when designing a table, basic table and multidimensional table.
To edit a table in the designer, go to the list of tables in Genus Studio, locate the table, and double click it, or right click and select Open.
To view the table definition in a read only mode, press and hold the CTRL+SHIFT keys when opening the table. This prevents the table from being locked for other modelers, and it is not possible to save any changes to the table.
Basic Table
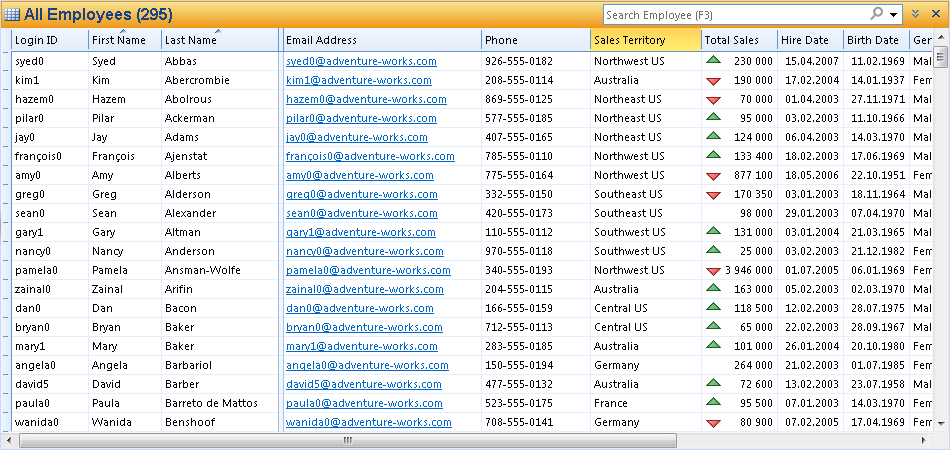
A basic table presents objects in a standard tabular format, where a column represents a field value for an object, and a row represents an object. The following table illustrates a basic table presenting employee data.
Multidimensional Table
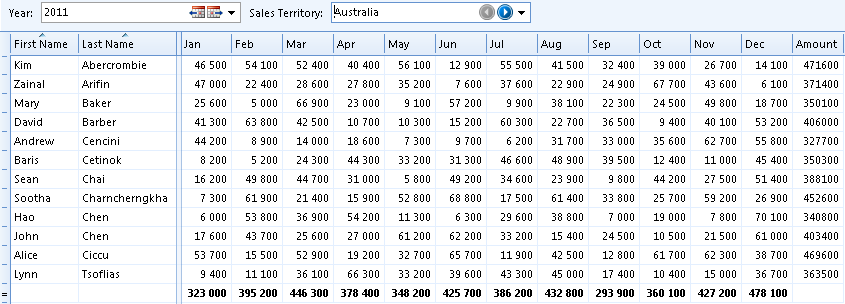
A multidimensional table presents objects with a common set of values laid out in a fixed number of rows and columns. The following table illustrates a multidimensional table, where sales quotas are allocated by employee and month.